Belly Fat Reduction for the "Thin-Fat" Indian Body Type
Finally Target the Stubborn Visceral Fat That Diets and Exercise Can’t Touch
- 4.8 Rating
- 6000+ Patients
- 7 Clinics
- IADVL Registered
- US-FDA Approved Tech
Why Your Belly Fat Won't Go Away (No Matter What You Try)
You’ve tried everything. Diets, gym, yoga, intermittent fasting. The weight comes off everywhere except your belly.
Sound familiar?
- Lose weight but belly stays the same
- Normal weight but look pregnant
- Clothes fit everywhere except the waist
- Family history of diabetes despite being “thin”
- Feeling tired even after sleeping well
The reason: You’re not dealing with regular fat. You’re dealing with visceral fat – the dangerous fat stored deep inside your abdomen, around your organs.
This is the “Thin-Fat Indian” problem. And it needs medical treatment, not another diet.
What is Visceral Fat? (And Why It's Killing Indians Silently)
Two Types of Belly Fat
Subcutaneous Fat
Under the skin
You can pinch it
Lower risk
Subcutaneous Fat
Around organs (liver, intestines, pancreas)
Subcutaneous Fat
Extremely dangerous
Why Visceral Fat is Deadly
- Releases inflammatory chemicals into your blood
- Causes insulin resistance (leads to diabetes)
- Increases heart disease risk by 3x
- Linked to fatty liver disease
- Connected to certain cancers
- Affects hormone balance
The Indian Problem
Indians store MORE visceral fat than other ethnicities – even at the same BMI.
Research Finding
- Indians have 2x more visceral fat than Europeans at the same weight
- One-third of “normal weight” Indians have dangerous visceral fat levels
- Indian diabetes rates are highest in the world – visceral fat is the main driver
The "Thin-Fat Indian" Phenotype Explained
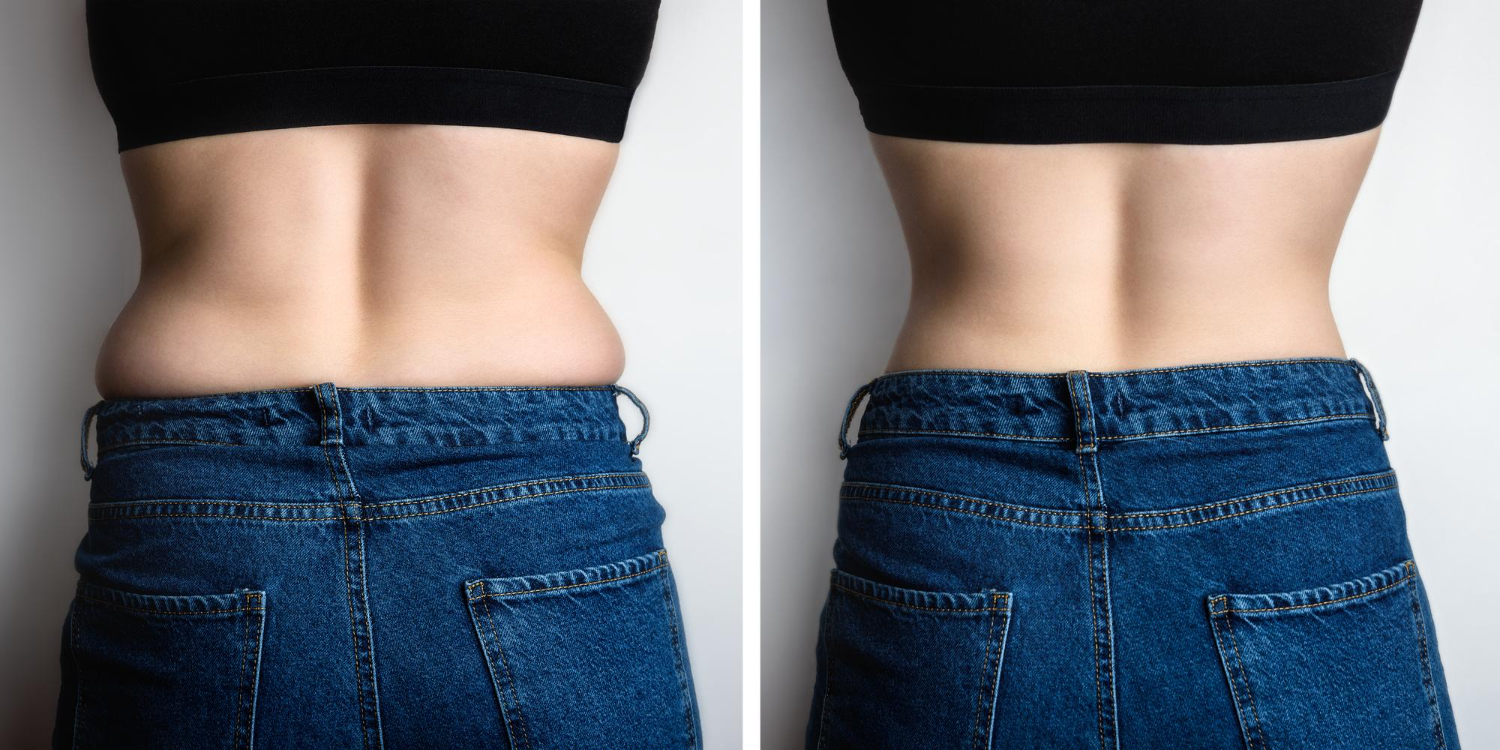
Signs You May Be "Thin-Fat":
- Normal BMI but big belly
- Weak arms and legs despite belly fat
- Feel tired and sluggish
- Pre-diabetic blood sugar readings
- High triglycerides, low HDL cholesterol
- Dark patches on neck (acanthosis nigricans)
- Skin tags appearing
- PCOS symptoms (women)
- Low testosterone symptoms (men)
What is "Thin-Fat" or "Skinny Fat"?
A person who:
- Looks thin or normal weight
- Has low muscle mass
- Has high body fat percentage
- Stores fat around organs (visceral)
- Has metabolic problems of an obese person
Person
BMI
Body Fat %
Indian Doctor
22.3
21.2%
European Doctor
22.3
9.1%
Why Does This Happen to Indians?
- Genetics: Indian bodies evolved for scarcity, store fat efficiently
- Diet: High carb, low protein traditional diets
- Lifestyle: Sedentary jobs, less physical activity
- Muscle Loss: Low protein intake = sarcopenia (muscle wasting)
- Stress: High cortisol = belly fat storage
Same BMI. The Indian had 2.3x more body fat.
Indian Belly Fat Risk Assessment
Waist Circumference (More Accurate Than BMI):
Category
Indian BMI
Indian BMI
Western BMI
Men
Below 78 cm
78-90 cm
Above 90 cm
Women
Below 72 cm
72-80 cm
Above 80 cm
Waist-to-Hip Ratio:
Gender
Healthy
High Risk
Men
Below 0.90
Above 0.90
Women
Below 0.85
Above 0.85
Obese
25+
30+
Visceral Fat Area (Measured by Scan):
Level
Risk
Below 100 cm²
Normal
100-150 cm²
Elevated
Above 150 cm²
High
Forget Western BMI Charts. Use Indian Standards:
Category
Indian BMI
Western BMI
Normal
Below 23
Below 25
Overweight
23 – 24.9
25 – 29.9
Obese
25+
30+
How to Measure Your Waist Correctly:
- Stand straight, breathe out normally
- Find the midpoint between your lowest rib and hip bone
- Wrap measuring tape around this point
- Tape should be snug but not tight
- Read measurement after exhaling
Why Diets Fail for Indian Belly Fat
The Biology Working Against You
- Hormonal Resistance
- High insulin = body stores fat, can’t burn it
- High cortisol = fat goes straight to belly
- Low adiponectin = poor fat metabolism
- Metabolic Adaptation
- Dieting slows metabolism
- Body fights to keep visceral fat
- Weight regain is almost guaranteed
- The Indian Diet Problem
- Rice/roti dominant = high glycemic load
- Low protein = muscle loss
- Frequent snacking = constant insulin spikes
Result: Visceral belly fat is RESISTANT to lifestyle changes alone. It needs medical intervention.
Medical Belly Fat Reduction: How It Works
The DermaVue SuperHuman Approach
Medical belly fat reduction targets the root cause – hormonal and metabolic dysfunction.
Comprehensive Assessment
What we measure:
- Body composition (fat vs muscle)
- Visceral fat area (cm²)
- Waist circumference
- Blood markers (insulin, HbA1c, lipids)
- Metabolic rate
- Muscle mass
Medical Treatment
GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Therapy:
- Medications: Semaglutide (Ozempic/Wegovy), Tirzepatide (Mounjaro)
- Specifically targets visceral fat
- Fixes hormonal imbalance
- Reduces hunger and cravings
- Doctor-supervised, prescription-only
Nutrition Optimization
The “Protein Anchor” Strategy:
- 1.2-1.6g protein per kg body weight
- 30g protein within 30 minutes of waking
- “Protein First” eating – protein before carbs
- Reduced glycemic load
Muscle Preservation
The “Anabolic Shield” Protocol:
- Resistance training 2x per week minimum
- Creatine supplementation (5g daily)
- Prevent muscle loss during fat loss
- Maintain metabolic rate
Monitoring & Adjustment
- Regular body composition scans
- Waist circumference tracking
- Ensure fat loss, NOT muscle loss
- Medication adjustments as needed
Expected Results for Belly Fat Reduction
| Realistic Timeline: | What Changes Beyond the Scale: | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Timeline | What to Expect | Marker | Typical Improvement |
| Week 1–2 | Reduced appetite, fewer cravings | Waist Circumference | 8–15 cm reduction |
| Month 1 | 2–4% weight loss, clothes feel looser | Visceral Fat Area | 30–50% reduction |
| Month 2 | Visible waist reduction begins | Fasting Blood Sugar | Normalized in most patients |
| Month 3 | 5–8% weight loss, significant waist reduction | HbA1c | Significant improvement |
| Month 6 | 10–15% weight loss, belt size down 2–3 notches | Triglycerides | 20–40% reduction |
| Month 12 | 15–22% weight loss, metabolic health normalized | Blood Pressure | Often reduces significantly |
| Energy Levels | Markedly improved | ||
| Sleep Quality | Better rest, less apnea | ||
Important: Results vary by individual. These are typical outcomes with full program compliance.
Who is a Good Candidate for Medical Belly Fat Reduction?
- BMI 23 or above (Indian standard)
- Waist circumference above 85 cm (men) or 75 cm (women)
- "Thin-fat" or "skinny-fat" body type
- Belly fat despite normal weight elsewhere
- Failed multiple diet/exercise attempts
- PCOS patients with weight-related symptoms
- Failed multiple diet and exercise attempts
- Family history of diabetes or heart disease
- Pre-diabetic or Type 2 diabetic
- PCOS with weight-related symptoms
- Metabolic syndrome
- Metabolic syndrome
- Fatty liver disease
- Acanthosis nigricans (dark neck patches)
- Skin tags
- Personal/family history of medullary thyroid cancer
- Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2
- History of pancreatitis
- Active gallbladder problems
- Pregnant or planning pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
- Under 18 years old
- Active eating disorder
Belly Fat Reduction vs Other Treatments
How Medical Weight Loss Compares:
| Treatment | Targets Visceral Fat? | Improves Metabolic Health? | Sustainable? | Doctor Supervised? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLP-1 Medical Treatment | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Diet Programs | ❌ Partially | ❌ Limited | ❌ Often rebounds | ❌ Usually not |
| Liposuction | ❌ No (surface only) | ❌ No | ❌ Fat can return | ✅ Surgical |
| CoolSculpting | ❌ No (surface only) | ❌ No | ⚠️ Limited areas | ⚠️ Varies |
| Tummy Tuck | ❌ No (skin only) | ❌ No | ⚠️ Cosmetic only | ✅ Surgical |
| Weight Loss Pills (OTC) | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No |
Why GLP-1 Treatment is Different
- For a 90kg person:
- Specifically reduces visceral fat (proven in clinical trials)
- Fixes the hormonal root cause
- Improves insulin sensitivity
- Reduces cardiovascular risk
- Sustainable with proper support
Nutrition Tips for Indian Belly Fat
Smart Swaps for South Indian Diet:
Kerala Matta rice (red rice)
Lower glycemic, more fiber
Parotta
Green tea / Black coffee
Protein Sources for Vegetarians:
The "Sunset Carb Rule"
- No rice or wheat after 6 PM
- Aligns with your body’s circadian rhythm
- Evening = lower insulin sensitivity
- Dinner: Protein + vegetables only
Your Treatment Journey at DermaVue
Initial Consultation (45-60 mins)
What happens:
- Complete medical history
- Physical examination
- Body composition analysis
- Waist circumference measurement
- Blood test orders
- Goal discussion
- Eligibility assessment
Diagnostic Testing
Tests may include:
- Fasting blood sugar & HbA1c
- Fasting insulin & HOMA-IR
- Lipid profile (including ApoB)
- Liver function tests
- Thyroid panel
- Body composition scan (BIA/DEXA)
Personalized Treatment Plan
Based on your results:
- Appropriate medication selection
- Dosing schedule
- Nutrition plan from dietitian
- Exercise guidance
- Follow-up schedule
Treatment & Monitoring
Ongoing support:
- Weekly dietitian check-ins
- Monthly doctor reviews
- Body composition tracking
- Medication adjustments
- Side effect management
Long-term Maintenance
After reaching goals:
- Medication tapering (if appropriate)
- Metabolic flexibility training
- Maintenance nutrition plan
- Ongoing monitoring
Medical Lead – Belly Fat Reduction Program
Dr. Sarath Chandran, MBBS, MD (DVL)
Dr. Sarath Chandran is the clinical lead for the SuperHuman Medical Weight Loss Program at DermaVue.
Expertise:
- Medical dermatology and metabolic health
- GLP-1 receptor agonist therapy
- Insulin de-escalation protocols
- Body composition optimization
Approach:
- Evidence-based treatment
- Personalized protocols
- Focus on muscle preservation
- Long-term metabolic health
Education:
- MBBS, MD (Dermatology, Venereology, Leprosy)
- Advanced training in metabolic medicine
- Certified in obesity management
Belly Fat Reduction at 7 DermaVue Locations
All Locations Offer:
- Board-certified physicians
- Body composition analysis
- Visceral fat measurement
- Dietitian consultations
- IADVL registered doctors
- US-FDA approved technologies
Frequently Asked Questions About Belly Fat Reduction
What is visceral fat and why is it dangerous?
Why can't I lose belly fat with diet and exercise?
What is the "thin-fat Indian" phenotype?
“Thin-fat” or “skinny fat” describes people who:
- Look thin or normal weight
- Have low muscle mass
- Have high body fat percentage (especially visceral)
- Have metabolic problems of an obese person
Research shows one-third of “normal weight” Indians are actually metabolically unhealthy due to hidden visceral fat. Standard BMI misses this danger.
How is medical belly fat reduction different from liposuction?
Medical Treatment | Liposuction |
Targets visceral (internal) fat | Only removes subcutaneous (surface) fat |
Improves metabolic health | No metabolic benefit |
Non-surgical | Surgical procedure |
Addresses root cause | Cosmetic only |
Sustainable results | Fat can return |
Liposuction cannot reach the dangerous visceral fat that causes health problems.
How much belly fat can I lose?
Typical results with full program compliance:
- Month 3: Waist reduced by 5-8 cm
- Month 6: Waist reduced by 8-12 cm
- Month 12: Waist reduced by 12-18 cm
Visceral fat area typically reduces by 30-50% over 12 months. Individual results vary based on starting point and adherence.
Will I lose muscle along with belly fat?
Not with our approach. The SuperHuman protocol includes:
- High protein intake (1.2-1.6g per kg)
- Creatine supplementation
- Resistance training guidance
- Regular body composition monitoring
We track muscle mass at every visit to ensure you’re losing fat, not muscle.
Is belly fat reduction treatment safe for diabetics?
Yes – often the best choice for diabetics. GLP-1 medications:
- Originally developed for diabetes
- Improve blood sugar control
- Reduce visceral fat specifically
- May allow reduction of diabetes medications
Our protocol includes safe insulin de-escalation when appropriate.
How long do I need treatment?
Treatment duration depends on:
- Starting visceral fat level
- Weight loss goals
- Metabolic health targets
Most patients see significant results in 6-12 months. Some may need longer for optimal outcomes. Your doctor will create a personalized timeline.
What are the side effects?
Common side effects (usually mild, temporary):
- Nausea (most common, reduces over time)
- Reduced appetite (part of how it works)
- Constipation (manageable with fiber)
- Occasional diarrhea
These typically decrease within 2-4 weeks as your body adjusts. Our team provides guidance throughout.
How much does belly fat reduction treatment cost?
Treatment costs vary based on:
- Medication selected (Ozempic vs Mounjaro)
- Duration of treatment
- Additional services needed
Initial consultation includes full assessment. Payment plans available. Contact us for current pricing.
Book Your Consultation
DermaVue Clinic Locations
- Kerala (6 Locations)
Thiruvananthapuram
Kollam
Thiruvalla
Kottayam
Kochi (Aluva)
- Tamil Nadu (1 Location)
DermaVue operates seven advanced dermatology clinics across Kerala and Tamil Nadu. Our physician-led team specializes in medical dermatology, cosmetic procedures, hair restoration, and now comprehensive metabolic health through the SuperHuman Program.
- Board-certified dermatologists
- IADVL registered physicians
- US-FDA approved technologies
- International safety protocols
- Privacy-first facilities
Medical Disclaimer: This information is educational and does not constitute medical advice. Individual results vary. All treatments require medical consultation. GLP-1 medications are prescription-only and require physician supervision.
Quick Links
Contact Us
Copyright © 2026 dermavue. All Rights Reserved.

